

Although the documentation has quite a lot to say on the subject, I feel it tries to introduce too many concepts at once and ends up being confusing, especially when it comes to choosing between VARRAYs and Nested Table collections, where most of the. Scan scan value into Jsonb, implements sql.Scanner interfaceįunc (j *JSON) Scan (value interfaceĭb.AddError(errors.New( "invalid encryption key")) Collection Types in PL/SQL I often see questions on technical forums about arrays in PL/SQL, which type to use and what the differences are.

Sql data type for an icollections how to#
The customized data type has to implement the Scanner and Valuer interfaces, so GORM knowns to how to receive/save it into the database
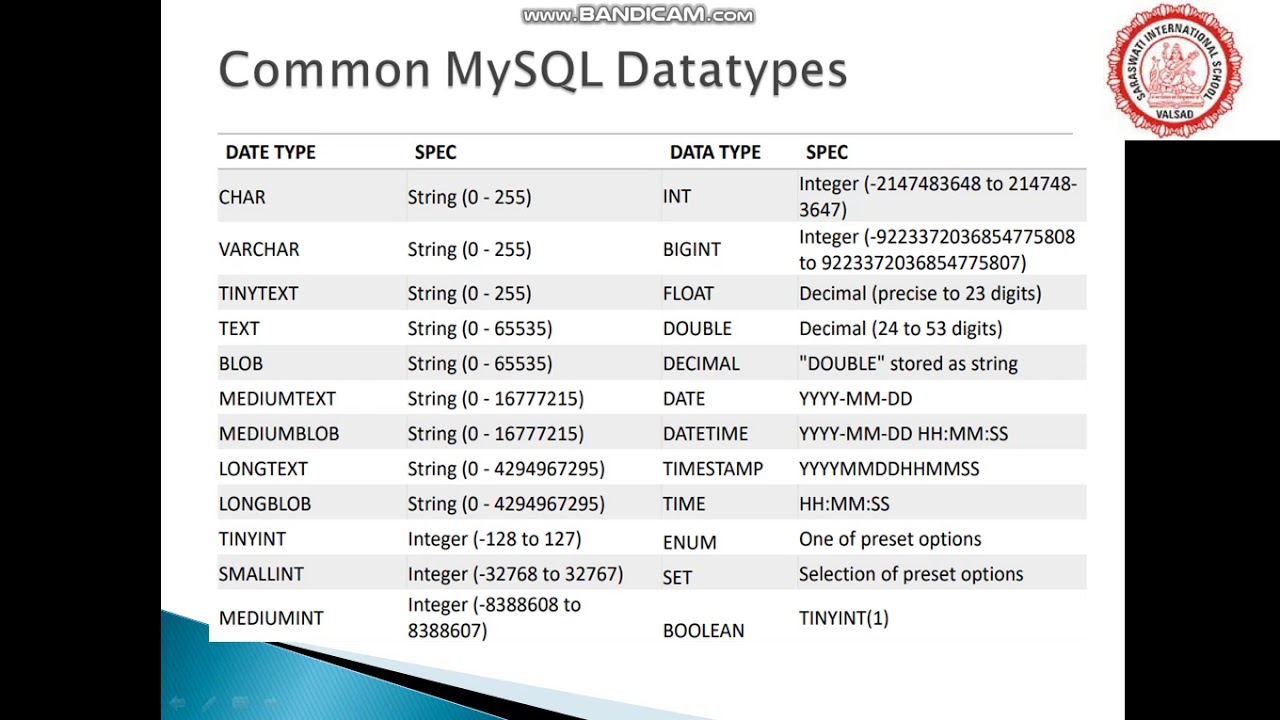
Note that above data types are not supported in MySQL database.GORM provides few interfaces that allow users to define well-supported customized data types for GORM, takes json as an example Implements Customized Data Type Scanner / Valuer Variable-length storage with a maximum size of 1GB data Variable-length storage with provided max characters
Variable-length storage with a maximum length of 4,000 characters SQL Unicode Character and String Data Types Datatypeįixed length with maximum length of 4,000 characters Note that all the above data types are for character stream, they should not be used with Unicode data. Variable-length storage with maximum size of 2GB data Variable-length storage with provided max characters, not supported in MySQL Variable-length storage with a maximum length of 8,000 characters SQL Character and String Data Types Datatypeįixed length with a maximum length of 8,000 characters Stores year in 2 digits or 4 digit format. Stores number of seconds passed since the Unix epoch (‘ 00:00:00’ UTC) Stores date and time information in the format YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS There are three types of collections: associative array. The collection items, which represent collection types, gather data from the appropriate data providers on the specified targets. Let’s look into different categories of SQL data types in detail. The element or the value contained in a cell can be of a valid SQL data type or a user-defined type. When data collection starts, SQL Server Agent spawns a process for the data collector, which in turn loads the Integration Services packages for the collection set. Idea is to have the knowledge of what data type to be used in a specific scenario.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
